Fear Killer Robots
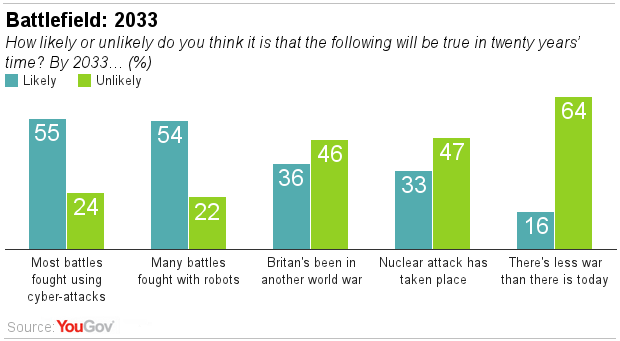
Despite overall opposition to allowing robots onto battlefields, most British adults (54%) expect them to be used in many battles within 20 years.
Recently, a broad group of several thousand academics, legal scholars, roboticists, and scientific luminaries – including Stephen Hawking – released an open letter warning that efforts to develop autonomous weapons could unleash a Pandora’s box of ills, from ethnic cleansing to pervasive arms races. Certainly, this is not a world in which any of us would like to live. But nor is it a world that rises inevitably from the development of autonomous weapons.
However, on the contrary, autonomous weapons could shape a better world, one in which the fog of war thins, if ever so slightly. These systems are not subject to the fatigue, combat stress, and other factors that occasionally cloud human judgment. And if responsibly developed and properly constrained, they could ensure that missions are executed strictly according to the rules of engagement and the commander’s intent. A world with autonomous weapons could be one where the principles of international humanitarian law (IHL) are not only respected but also strengthened.
The key to avoiding the catastrophes predicted in the letter is restricting what such a weapon can and can’t do. It might, for example, be allowed to operate only for a limited time or in a limited geographic area — perhaps underwater or in other areas in which civilians are not present. This would, in turn, increase a commander’s control over the weapon and strengthen accountability for the system’s use – a key concern among advocates of a ban on autonomous weapons. These machines could also be designed to target only military hardware, thereby strengthening adherence to the IHL principles of proportionality and distinction and further reducing civilian casualties.
These positive outcomes are possible only if the international community offers careful stewardship. First and most importantly, states will need to agree upon a definition of “autonomous weapons.” At the recent UN meeting on Lethal Autonomous Weapon Systems, governments and non-governmental organizations expressed widely divergent, and frequently incompatible, notions of autonomy and autonomous weapons.
Some argued that existing systems qualify as autonomous, while others, such as the United Kingdom, argued that they “do not and may never” exist. Clarifying the definition will be critical to advancing the dialogue and to establishing responsible design requirements and operating parameters.
Second, governments must ensure that meaningful human control exists over their autonomous weapons. As Michael Horowitz and Paul Scharre have written in their primer on the subject, this should include standards that help operators make deliberate, legal, and moral decisions about the use of force.
Third, governments should implement strict testing and evaluation standards to ensure that any weapon that can autonomously pick a target or begin an engagement performs as intended, and that procedures for its use are clear to operators. In order to ensure that such systems continue to operate in accordance with their design features, governments should agree to periodic testing in realistic operating environments.
Finally, it will be essential for governments to further explore the ways in which accountability for the use of autonomous weapons can be established and enforced. While such an undertaking will be undoubtedly challenging, it will be critical in ensuring that the use of these systems adheres to IHL and reducing potential risks.
Despite the somewhat breathless tone of the letter, its signatories draw attention to an important technological development that the international community would do well to address in a measured and calm way. Autonomous weapons will never remove the human dimension of warfare, but if we are careful, they just might thin the fog.


























